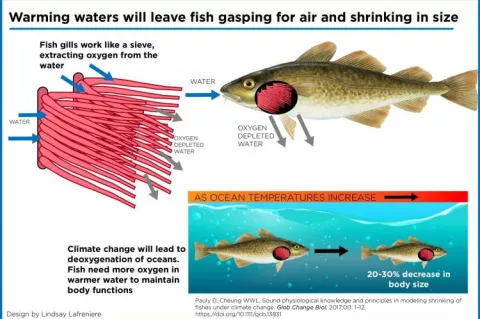
Warmer weather shrinks fish
This is the findings of a new study in Global Change Biology by the University of British Columbia. The reason for this future decline in size stems from the fact that fish are cold-blooded animals, and are thus unable to regulate their body temperatures.
“When their waters get warmer, their metabolism accelerates and they need more oxygen to sustain their body functions,” said co-author William Cheung, associate professor at the Institute for the Ocean and Fisheries and director of science for the Nippon Foundation-UBC Nereus Program.