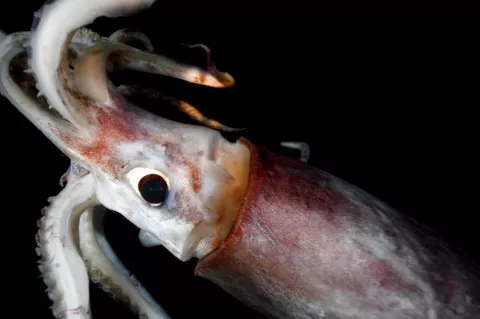
What do vampire squids eat (it's not what you think)
The vampire squid (Vampyroteuthis infernalis) is a small, deep-sea cephalopod found throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world. It's easy to imagine the vampire squid as a nightmarish predator. It lurks in the eternal midnight of the deep sea, has a dark red body, huge blue eyes, and a cloak-like web that stretches between its eight arms.